Heritability in Psychiatric Illness and the Role of Family Counselling
 Understanding risk without blame, and care without control
Understanding risk without blame, and care without control
Psychiatric illnesses often raise difficult questions within families.
“Is this genetic?”
“Did we cause this?”
“Will others in the family be affected?”
These questions reflect concern, not culpability. Modern psychiatry offers clearer answers today—answers that reduce guilt, correct myths, and highlight the central role families play in recovery.
This article explains heritability in psychiatric illness in simple terms and outlines how family counselling is practically conducted in clinical settings.
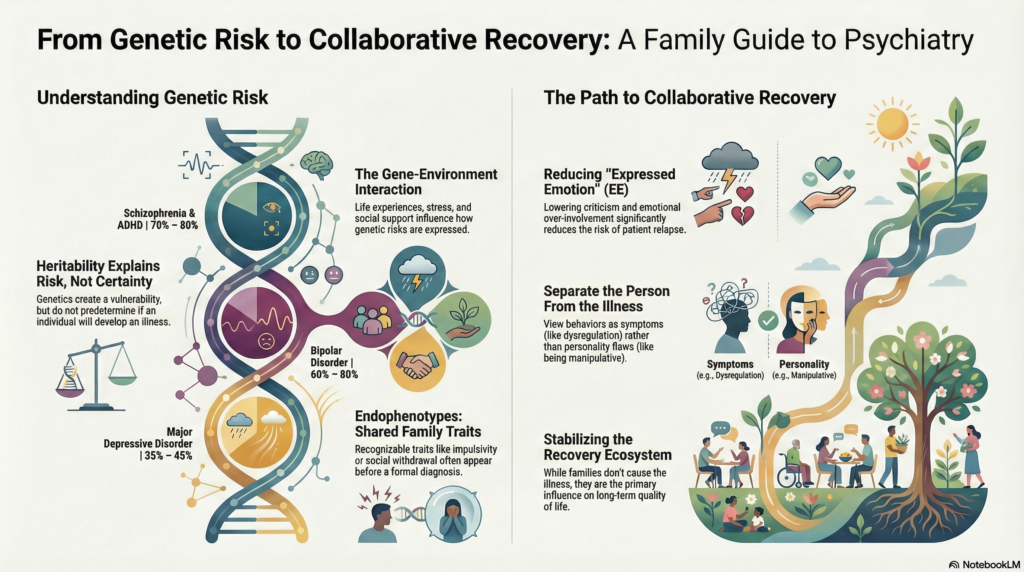
What Does Heritability Mean in Psychiatry?
Heritability refers to the degree to which genetic factors contribute to differences in risk for an illness within a population. It does not mean that a condition is inevitable or fully predetermined.
For example:
-
Schizophrenia: ~70–80% heritability
-
Bipolar disorder: ~60–80%
-
Major depressive disorder: ~35–45%
-
ADHD: ~70–80%
These figures indicate that genetic vulnerability plays a substantial role, but they do not predict whether a particular individual will develop the illness.
Heritability explains risk, not certainty.
Psychiatric Illness Is Not Caused by a Single Gene
Unlike many inherited medical conditions, psychiatric disorders are:
-
Polygenic (involving many genes with small effects)
-
Non-specific (the same genes may increase risk for different conditions)
-
Environment-sensitive (life experiences influence expression)
This explains why:
-
Illness may skip generations
-
Siblings may develop different disorders—or none at all
-
Severity and age of onset vary within the same family
Genes create vulnerability; life circumstances shape outcome.
Gene–Environment Interaction: Where Families Matter Most
Psychiatric illness emerges through interaction between genetic risk and environmental factors such as:
-
Childhood adversity
-
Chronic stress
-
Substance use
-
Social support
-
Family emotional climate
The same genetic predisposition can lead to very different outcomes depending on the surrounding environment. This is where family involvement becomes crucial.
Endophenotypes: Shared Traits Within Families
Families often notice certain traits long before illness appears:
-
Emotional sensitivity
-
Impulsivity
-
Social withdrawal
-
Cognitive rigidity
-
Poor stress tolerance
These are known as endophenotypes—heritable traits that increase vulnerability but are not illnesses themselves. Recognising this helps families understand that behaviour is not sudden or deliberate, but part of a longer developmental pattern.
Why Family Counselling Is Essential in Psychiatry
Family counselling is not about assigning blame or delivering lectures. Its purpose is to reshape the emotional and interpersonal environment in which recovery occurs.
1. Creating a Shared Understanding
The first goal is to align everyone around a common explanatory model:
-
Psychiatric illness is a medical condition
-
Nobody is at fault
-
Families cannot control the illness, but they can influence outcomes
This reduces conflict and emotional polarization.
2. Reducing High Expressed Emotion (EE)
High expressed emotion—characterised by criticism, hostility, or excessive emotional involvement—is a well-established risk factor for relapse, particularly in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder.
Family counselling focuses on:
-
Reducing chronic criticism
-
Avoiding repeated confrontations
-
Limiting emotional over-involvement
-
Encouraging calm, predictable communication
Lower emotional intensity leads to better stability.
3. Separating the Person From the Illness
Families often unintentionally equate symptoms with personality:
-
“He is lazy” instead of “He is experiencing avolition”
-
“She is manipulative” instead of “She is emotionally dysregulated”
Counselling helps families externalise symptoms, preserving dignity and reducing power struggles.
4. Improving Symptom Awareness
Families are taught to recognise:
-
Early warning signs of relapse
-
Stress-related deterioration
-
Medication side effects
-
When to observe and when to seek help
This transforms families into effective support systems rather than constant monitors.
5. Boundary Setting and Role Balance
Support does not mean unlimited accommodation. Family counselling addresses:
-
Over-protectiveness
-
Burnout in caregivers
-
Loss of autonomy in patients
-
Clear but compassionate boundary setting
Healthy limits protect both the patient and the family.
6. Addressing Guilt, Grief, and Fear
Many families silently carry:
-
Genetic guilt
-
Grief for altered life expectations
-
Fear of chronic illness
-
Social stigma and secrecy
Counselling provides space to process these emotions so they do not translate into frustration, resentment, or disengagement.
7. Planning for Long-Term Care
Psychiatric illnesses often follow a fluctuating course. Family counselling shifts focus from:
-
“Cure vs failure”
to -
“Phases, recovery, and adaptation”
Relapse is reframed as information—not catastrophe.
A Key Clinical Insight
Medication treats neurobiology.
Psychotherapy supports psychological integration.
Family counselling stabilises the ecosystem in which both must function.
Families do not cause psychiatric illness—but they profoundly influence recovery, relapse prevention, and quality of life.
Closing Perspective
Understanding heritability allows families to move from guilt to responsibility, from blame to collaboration. When families learn to respond rather than react, psychiatric treatment becomes significantly more effective.
In psychiatry, recovery is rarely an individual achievement—it is often a family process done well.
Dr. Srinivas Rajkumar T, MD (AIIMS), DNB, MBA (BITS Pilani)
Consultant Psychiatrist & Neurofeedback Specialist
Mind & Memory Clinic, Apollo Clinic Velachery (Opp. Phoenix Mall)
✉ srinivasaiims@gmail.com 📞 +91-8595155808