How Does Caffeine Work? Benefits, Mechanisms, and Potential Risks
Caffeine is a natural stimulant found in coffee, tea, and energy drinks, and it’s one of the most widely consumed substances globally. Known for its ability to boost alertness and improve physical performance, caffeine plays a significant role in daily life. But how does caffeine work, and what are its benefits and risks? Let’s dive into the science behind this remarkable compound.
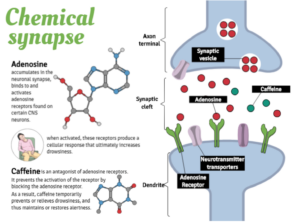
How Caffeine Works in the Body
After consumption, caffeine is quickly absorbed into the bloodstream and reaches the brain, where it blocks adenosine, a neurotransmitter responsible for promoting relaxation and sleepiness. By occupying adenosine receptors, caffeine prevents fatigue and increases alertness. This mechanism also stimulates the release of dopamine and norepinephrine, which enhance mood and focus.
Additionally, caffeine impacts physical performance by increasing adrenaline levels, enhancing heart rate, and improving blood flow. This combination prepares the body for physical exertion and sustains energy levels during activities.
Benefits of Caffeine
1. Boosts Mental Alertness
Caffeine improves concentration, reaction time, and cognitive function, making it a popular choice for productivity and study sessions.
2. Enhances Physical Performance
Caffeine reduces perceived effort during exercise and increases endurance by mobilizing fat stores for energy. It also strengthens muscle contractions by enhancing calcium release within muscle cells.
3. Protective Health Effects
Moderate caffeine consumption has been linked to a reduced risk of Parkinson’s disease and may protect against certain neurodegenerative disorders. It can also promote longevity when consumed as part of a balanced lifestyle.
4. Improves Mood
By stimulating dopamine production, caffeine can reduce feelings of fatigue and uplift mood, which is why it’s often considered a “feel-good” substance.
Potential Risks and Side Effects of Caffeine
While caffeine offers several benefits, excessive intake can lead to:
Anxiety and Restlessness: Overconsumption can increase jitteriness and nervousness.
Insomnia: Drinking caffeine late in the day may disrupt sleep patterns.
Digestive Issues: Sensitive individuals may experience acid reflux or stomach discomfort.
Dependency: Prolonged use can lead to withdrawal symptoms like headaches and irritability.
Heart Health Concerns: High doses may elevate heart rate and blood pressure, especially in people with pre-existing conditions.
Safe Caffeine Consumption
For most adults, up to 400 mg of caffeine per day—equivalent to about four cups of coffee—is considered safe. However, sensitivity varies. Pregnant women and those with certain medical conditions should consult healthcare providers for tailored advice. To minimize side effects, limit caffeine consumption in the late afternoon and avoid combining it with other stimulants.
Caffeine Timing for Maximum Benefits
To optimize performance and alertness, consume caffeine 30–60 minutes before physical or mental activities. This allows the substance to be fully absorbed into the bloodstream, delivering peak effects.
Conclusion
Caffeine is a powerful and versatile stimulant that can enhance both mental and physical performance when consumed responsibly. By understanding how caffeine works and monitoring your intake, you can harness its benefits while minimizing potential risks. Whether you’re seeking an energy boost, better focus, or improved workout performance, caffeine remains a popular choice for millions worldwide.